National Conference on Primary Health Care Education
Meeting: Family Medicine as the Care-Coordinator of Primary Health Care
and Its Implementation in Indonesian Higher Education Institutions"
Component 1. – Health Professional Education Quality (HPEQ Project)
Sub Component 1.2 – Development of Undergraduate Medical Education and Competency Standard
Makassar, 19 November 2012
BACKGROUND
One target of component 1-HPEQ program is the development of medical curriculum and competency standard. HPEQ, actually has conducted many meetings and preparations due to those points. Moreover, it also has its responsibility towards the establishment of "next SKDI" standard for medical students. But, before we move to our further journey, lets we rethink of our existing undergraduate medical curriculum, is it still reliable for 6 years ahead? Is it well prepared? Or, do we have to do something related to the nation development, especially in facing the universal coverage (SJSN) in 2014.
Looking back on the spirit of Alma Ata Declaration, 1978, entitled "The Health for All", which is stated that the main tasks of Indonesian national health sector are to maintain and to improve health care services for every citizen in Indonesia. To accomplish this, the health care system must prioritize promotion and preventive services along with disease management and rehabilitative efforts. To achieve this vision, the Indonesian national health system has some missions to carry out: (1) developing a medical system that is consistent with the national vision, (2) encouraging healthy life styles for both the individual and the community, (3) maintaining and improving individual, family and society including environmental health and the main point, (4) improving physician training and providing high quality and affordable health care regardless of the economic means of the family or community. It is a big dream, and need a systematic approach to make it real.
In line with this spirit, WHO on its report in 2008 stated that the main actor of country health status is the Primary Health Care. it is also stated that there are 4 pillars in the establishment of this sector: universal coverage, medical service, good leadership and policy. From this point, the main responsibility of Medical Faculty can be "how to produce the graduate doctor who can guide Indonesian people to reach their qualified health service". This initiative cannot be separated from interdisciplinary cooperation between education and health system perspective.
Previously, the SKDI standard (KKI, 2006) stated that the undergraduate medical curriculum should be oriented to family medicine, but what kind of the "family medicine/family doctor oriented" they want to produce? What kind of the family doctor that they want to use in guiding the SJSN? If, the government wants to use the existing doctors, whether they are able to overcome the patient's problem? Or do they need a special skill in primary health care level?
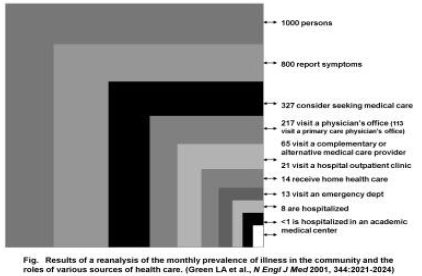
In the other hand, still focused on problems, list of diseases and statement of "family medicine oriented curriculum", it also lacks of the involvement of 7 areas of competencies such communication, and doctors awareness of patient as a member of their community. The education process still also focused on the teaching hospital. It is good, but may impact on the risk that graduate doctors meet many difficulties in handling patients in real cases. Green et al (2001) stated that the cases in teaching hospital are only represented 1% problems in the community. The arrangement of early exposure in primary care and community could be the best answer as the patient live in those settings.
Herewith we also want to explain the comparison of education between the primary care doctor and
other specialists:
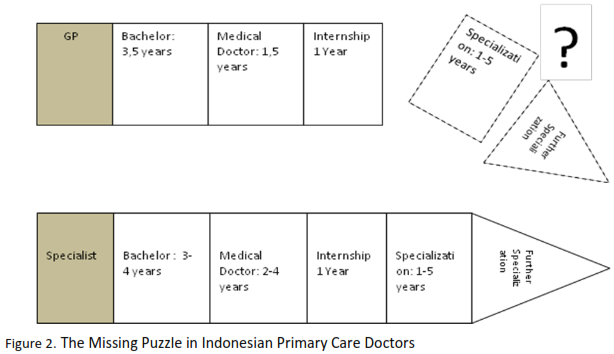
From those points, the educational aspect plays the important role in guiding the SJSN 2014. It is, of course take time but not an impossible thing to achieve.
Previously, several meetings to rethink our Primary Health Care were held based on HPEQ project, from those, the consortium committee agreed to revitalize the Indonesian PHC condition as stated in the DECALARATION TOWARDS BETTER PHC WITH FAMILY DOCTORS AS THE CARE KOORDINATORS (Jakarta 22 September 2012). They also had prepared its implementation in Indonesian Higher Education Institutions through educational and supporting document policies framework.
AIMS :
- A national initiative towards accessible high quality primary health care with family doctors as the backbone for every citizen of Indonesia
- To prepare of Indonesian medical faculties in implementing family medicine in their medical curriculum from undergraduate medical education to postgraduate family medicine masters and specialization
- To build the critical mass and home-base for general practitioners and family doctors in Indonesia.
MEASURABLE OUTCOME
The commitment of Indonesian medical faculties in the implementation of family medicine educational approaches from undergraduate to postgraduate levels.
DATE AND PLACE
This conference meeting will be held on :
Date : 19 November 2012
Place : Makassar
DETAIL SCHEDULE(S)

